[leetcode] 687. Longest Univalue Path
2023. 3. 2. 13:45ㆍ노트/Algorithm : 알고리즘

Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest path, where each node in the path has the same value. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of the path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Example 1:
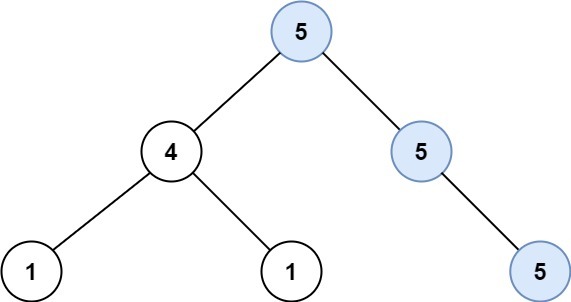
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,null,5]
Output: 2
Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 5).
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,null,5]
Output: 2
Explanation: The shown image shows that the longest path of the same value (i.e. 4).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 104].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- The depth of the tree will not exceed 1000.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
result = 0
def longestUnivaluePath(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(node):
if node is None:
return 0
# 존재하지 않는 노드까지 DFS 재귀 탐색
left = dfs(node.left)
right = dfs(node.right)
# 현재 노드가 자식 노드와 동일한 경우 거리 1 증가
if node.left and node.left.val == node.val:
left += 1
else:
left = 0
if node.right and node.right.val == node.val:
right += 1
else:
right = 0
# 왼쪽과 오른쪽 자식 노드 간 거리의 합 최댓값이 결과
self.result = max(self.result, left + right)
return max(left, right)
dfs(root)
return self.result'노트 > Algorithm : 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [leetcode] 617. Merge Two Binary Trees (0) | 2023.03.09 |
|---|---|
| [leetcode] 226. Invert Binary Tree (0) | 2023.03.09 |
| [leetcode] 543. Diameter of Binary Tree (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| [leetcode] 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (0) | 2023.02.23 |
| [leetcode] 787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops (0) | 2023.02.22 |